Scientists have demonstrated a clear link between the 11-year sun cycle and winter weather over the northern hemisphere for the first time.
This move will speed the creation of thousands of construction and operations jobs while transforming the nation’s electric system into a modern, 21st century grid that is safer and more secure, and gives consumers more energy choices.
A Californian-based study has looked in detail at air quality and the impact of traffic-related air pollution on premature birth.

How can the largest university in Dallas-Fort Worth, Texas, lead the pack in sustainability? Build a green football stadium, of course.
Drinking water taken from a deep aquifer protected by a semi-permeable layer of rock should be protected from many contaminants, including viruses. But viruses have been discovered in many deep Madison, Wis., water wells.
Combining recently launched green technology for navigating the oceans with the need to address gaps in critical earthquake information across the globe, scientists from Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego have been granted $1.02 million from the National Science Foundation to develop a cutting-edge deep-ocean seismic system.
In the waters along Florida’s east and west coasts, Florida State University (FSU) marine biologists are collecting new data on the once severely overfished Atlantic goliath grouper, a native species that is making a comeback in the southeastern United States after a 21-year moratorium on its capture while remaining critically endangered everywhere else in the world.
The Earth currently has more than 400 so-called "dead zones"--huge expanses of deep ocean that, because of human activities, become too oxygen-starved during the summer to support most life.
Sperm whales are classified as “endangered” under the Endangered Species Act and are listed on Appendix I of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora.
An Illinois research team has succeeded in overcoming one major obstacle to a promising technology that simultaneously reduces atmospheric carbon dioxide and produces fuel.
A new research program funded by the National Institutes of Health will explore the role that a changing climate has on human health.
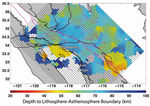
The geologic forces that shape the Earth's surface do their work in the lithosphere, often out of sight and far below the surface. Researchers have now measured the lithosphere’s thickness in southern California. It varies widely, from less than 25 miles to nearly 60 miles.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recently announced funding for Great Lakes Restoration Initiative projects in Northern Michigan totaling $1.1 million.
The Gulf Coast Ecosystem Restoration Task Force, chaired by U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Administrator Lisa P. Jackson, recently released for public review and feedback its comprehensive preliminary strategy for long-term ecosystem restoration.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency announced today that it has approved new performance standards for controlling urban stormwater runoff in Washington, D.C.
New research shows how trees can improve air quality by filtering out pollution particulates, which are damaging to human health.
Constructing buildings, power plants and roads has driven a substantial increase in China's CO2 emission growth.
In a Q&A session with scientists from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, the team examines the carbon presence in soil in relation to climate change.

A new study has shown that encouraging strips of wild plants at the edges of fields is important for supporting bees and other important pollinators.
Research suggests soil environment determines humus depletion, which means the question as to how soils respond to global climate change needs to be readdressed.